The vulva is the external part of the female genitals, including the clitoris, the vaginal lips, the opening to the vagina, and the surrounding skin and tissue. Most vulvar cancers are squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cancer begins in squamous cells (thin, flat skin cells) and is usually found on the vaginal lips. A small number of vulvar cancers are adenocarcinomas (cancers that begin in cells that make mucus and other fluids). This type of cancer is usually found on the sides of the vaginal opening.Vulvar cancer usually forms slowly over a number of years. Abnormal cells can grow on the surface of the vulvar skin for a long time. This condition is called vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). Because it is possible for VIN to become vulvar cancer, it is important to get treatment.
Women with vulvar cancer may experience the following symptoms or signs. Sometimes, women with vulvar cancer do not have any of these changes.
These are common symptoms in women who have developed vulvar cancer.
These symptoms may be caused by cancer or by other health problems. It is important for a woman to see her doctor if she is having any of these symptoms.
Local Physical examination is the first step in diagnosing vulvar cancer. In the examination, the doctor inspects the vulva and then feels the uterus, vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, and rectum to check for any unusual changes.
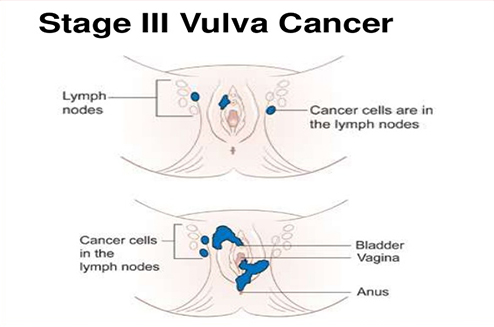
Sometimes there is swelling in groins and doctor may advice biopsy of the node. This biopsy can be radical or sentinel.
Vulvar biopsy detects type of cancer and its potential treatment plan.
The main treatment for vulvar cancer is surgery. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy may be used if the cancer cannot be entirely removed with surgery, if the cancer has a high risk for recurrence, and/or if the lymph nodes are involved with cancer.
If the tumor has spread to the point that initial surgical removal is not possible, sometimes the patient’s treatment plan starts with radiation therapy, often with simultaneous low-dose chemotherapy given weekly during the radiation treatments. Surgical removal of the vulvar lesion sometimes considered if the entire tumor does not go away after these treatments.Surgical options for invasive vulvar cancer include the removal of part or all of the vulva, depending on the size and spread of the primary tumor. This is called a vulvectomy.
Women with vulvar cancer may have concerns about if and how these treatments may affect their sexual function and fertility (ability to have children). These topics are important and should be discussed with the health care team before treatment begins.
Radical Local Excision of the Vulva: This surgery is done to remove the tumor and a large amount of tissue around it, called a margin. It is used for most primary tumors that are less than 4 centimeters (cm) in diameter and are either stage I or stage II disease.
Modified Radical Vulvectomy: This term describes a surgical procedure in which less than the full vulva is removed. For example, in a radical hemivulvectomy, only one side of the vulva is removed.
Radical Vulvectomy: A radical vulvectomy is the removal of part or all of the vulva, along with the underlying deep tissue. This is a very uncommon operation because most vulvectomies are modified in some way, and very large tumors are usually treated with chemoradiation, as described below.
Laser surgery is the use of a focused beam of light that vaporizes a premalignant skin lesion. It cannot be used to treat an invasive tumor.
Lymphadenectomy: this is a surgical procedure to remove lymph nodes in the groin in order to check for cancer.