Cancer occurs when cells in an area of the body grow abnormally. Ovarian cancer is the seventh most common cancer among women. There are three types of ovarian cancer:
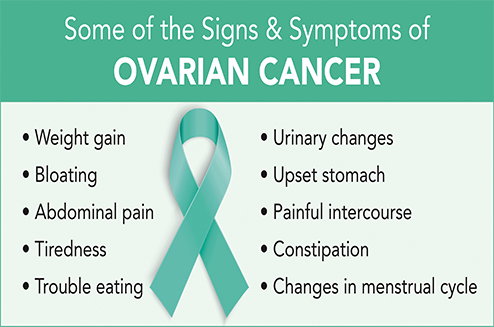
These symptoms include:
Women who have these symptoms almost daily for more than a few weeks should see their doctor, Prompt medical evaluation may lead to detection at the earliest possible stage of the disease. Early stage diagnosis is associated with an improved prognosis.
Familial breast-ovarian cancer syndrome is a common inherited condition that causes 10 % of all ovarian cancers and 5–10 percent of all breast cancers. Research confirms that there is a link between breast and ovarian cancer Any woman who has had one of these cancers is at a higher risk for developing the other.
When a woman experiences concerning symptoms, a pelvic exam, including a rectovaginal exam, and a general physical exam should be performed. If the exam is abnormal, women should undergo a transvaginal or pelvic ultrasound to evaluate the ovaries. If an abnormality of the ovaries is found, additional radiographic studies, such as a CT scan, or MRI and a blood
Test for CA 125, may be performed. CA 125 is elevated in approximately 80 % of women with advanced stage epithelial ovarian cancer, but elevations can occur for reasons other than ovarian cancer.
When ovarian cancer is diagnosed, it is important to determine if the cancer has spread beyond the ovaries. Your treatment team may do more tests to determine if the cancer has spread. In addition, during surgery, certain additional steps should be performed to determine the extent of the disease. This process is called staging. Staging helps to determine the exact extent of your cancer and what treatment plan is best for you. It is important that your surgery be performed by a Surgical oncologist (Cancer Surgeon)
Following surgery, your cancer will be categorized into one of the following stages:
Stage I : The cancer is found in one or both ovaries. Cancer cells also may be found on the surface of the ovaries or in fluid collected from the abdomen.
Stage II : The cancer has spread from one or both ovaries to other tissues in the pelvis, such as the fallopian tubes or uterus. Cancer cells may also be found in fluid collected from the abdomen.
Stage III : The cancer has spread outside the pelvis or nearby lymph nodes. Most commonly the cancer spreads to the omentum (an apron of fatty tissue that hangs down from the colon and stomach, diaphragm, intestine and the outside (surface) of the liver.
Stage IV :The cancer has spread to tissues outside the abdomen and pelvis. Most commonly to the space around the lungs. If the cancer spreads inside the liver or spleen, it is considered stage IV.
Ovarian cancer is most often treated with surgery and chemotherapy. Only rarely is radiation therapy used. It is important to distinguish between early stage ovarian cancer and advanced disease because the treatment depends upon your stage grade and performance score
Surgery is usually the first step in treating ovarian cancer. Most surgery is performed using a procedure called a laparotomy during which the surgeon makes a long cut in the wall of the abdomen.If ovarian cancer is found, the following procedures are performed
Primary cytoreductive surgery or Interval Debulking encompasses removing the bulk of tumor, removal of uterus, both tube and ovaries, omentum, pelvic and para aortic nodes. Sometimes chemotherapy might be needed before surgery, this is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Sometimes the surgery is extensive,and includs removal of portions of the small or large intestine and removal of tumor from the liver, diaphragm and pelvis. Removal of as much tumor as possible is one of the most important factors affecting cure rates. If you have early Stage I cancer, and still hope to get pregnant, it may be possible to only remove one ovary and fallopian tube. Your future pregnancy wishes should be discussed with your oncologist
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy for ovarian cancer is usually given intravenously (injected into a vein). Chemotherapy is usually given in cycles. Periods of chemotherapy treatment are alternated with rest periods when no chemotherapy is given. Most women with ovarian cancer receive chemotherapy for about 6 months following their surgery. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given before surgery in advanced ovarian cancer. What are